K8S中Pod是最小单位,如何书写一个Pod,可以利用kubectl的explain命令
kubectl explain pod
会贴出书写Pod的yaml所需的参数
kubectl explain pod
| KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 DESCRIPTION: Pod is a collection of containers that can run on a host. This resource is created by clients and scheduled onto hosts. FIELDS: apiVersion <string> APIVersion defines the versioned schema of this representation of an object. Servers should convert recognized schemas to the latest internal value, and may reject unrecognized values. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#resources kind <string> Kind is a string value representing the REST resource this object represents. Servers may infer this from the endpoint the client submits requests to. Cannot be updated. In CamelCase. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#types-kinds metadata <Object> Standard object’s metadata. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#metadata spec <Object> Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status status <Object> Most recently observed status of the pod. This data may not be up to date. Populated by the system. Read-only. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status |
然后分别的统计spec和metadata所需的字段,比如
kubectl explain pod.spec
| KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: spec <Object> DESCRIPTION: Specification of the desired behavior of the pod. More info: https://git.k8s.io/community/contributors/devel/sig-architecture/api-conventions.md#spec-and-status PodSpec is a description of a pod. FIELDS: activeDeadlineSeconds <integer> Optional duration in seconds the pod may be active on the node relative to StartTime before the system will actively try to mark it failed and kill associated containers. Value must be a positive integer. affinity <Object> If specified, the pod’s scheduling constraints automountServiceAccountToken <boolean> AutomountServiceAccountToken indicates whether a service account token should be automatically mounted. containers <[]Object> -required- List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be updated. dnsConfig <Object> Specifies the DNS parameters of a pod. Parameters specified here will be merged to the generated DNS configuration based on DNSPolicy. dnsPolicy <string> Set DNS policy for the pod. Defaults to “ClusterFirst”. Valid values are ‘ClusterFirstWithHostNet’, ‘ClusterFirst’, ‘Default’ or ‘None’. DNS parameters given in DNSConfig will be merged with the policy selected with DNSPolicy. To have DNS options set along with hostNetwork, you have to specify DNS policy explicitly to ‘ClusterFirstWithHostNet’. enableServiceLinks <boolean> EnableServiceLinks indicates whether information about services should be injected into pod’s environment variables, matching the syntax of Docker links. Optional: Defaults to true. ephemeralContainers <[]Object> List of ephemeral containers run in this pod. Ephemeral containers may be run in an existing pod to perform user-initiated actions such as debugging. This list cannot be specified when creating a pod, and it cannot be modified by updating the pod spec. In order to add an ephemeral container to an existing pod, use the pod’s ephemeralcontainers subresource. This field is alpha-level and is only honored by servers that enable the EphemeralContainers feature. hostAliases <[]Object> HostAliases is an optional list of hosts and IPs that will be injected into the pod’s hosts file if specified. This is only valid for non-hostNetwork pods. hostIPC <boolean> Use the host’s ipc namespace. Optional: Default to false. hostNetwork <boolean> Host networking requested for this pod. Use the host’s network namespace. If this option is set, the ports that will be used must be specified. Default to false. hostPID <boolean> Use the host’s pid namespace. Optional: Default to false. hostname <string> Specifies the hostname of the Pod If not specified, the pod’s hostname will be set to a system-defined value. imagePullSecrets <[]Object> ImagePullSecrets is an optional list of references to secrets in the same namespace to use for pulling any of the images used by this PodSpec. If specified, these secrets will be passed to individual puller implementations for them to use. For example, in the case of docker, only DockerConfig type secrets are honored. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod initContainers <[]Object> List of initialization containers belonging to the pod. Init containers are executed in order prior to containers being started. If any init container fails, the pod is considered to have failed and is handled according to its restartPolicy. The name for an init container or normal container must be unique among all containers. Init containers may not have Lifecycle actions, Readiness probes, Liveness probes, or Startup probes. The resourceRequirements of an init container are taken into account during scheduling by finding the highest request/limit for each resource type, and then using the max of of that value or the sum of the normal containers. Limits are applied to init containers in a similar fashion. Init containers cannot currently be added or removed. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/init-containers/ nodeName <string> NodeName is a request to schedule this pod onto a specific node. If it is non-empty, the scheduler simply schedules this pod onto that node, assuming that it fits resource requirements. nodeSelector <map[string]string> NodeSelector is a selector which must be true for the pod to fit on a node. Selector which must match a node’s labels for the pod to be scheduled on that node. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/assign-pod-node/ overhead <map[string]string> Overhead represents the resource overhead associated with running a pod for a given RuntimeClass. This field will be autopopulated at admission time by the RuntimeClass admission controller. If the RuntimeClass admission controller is enabled, overhead must not be set in Pod create requests. The RuntimeClass admission controller will reject Pod create requests which have the overhead already set. If RuntimeClass is configured and selected in the PodSpec, Overhead will be set to the value defined in the corresponding RuntimeClass, otherwise it will remain unset and treated as zero. More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/20190226-pod-overhead.md This field is alpha-level as of Kubernetes v1.16, and is only honored by servers that enable the PodOverhead feature. preemptionPolicy <string> PreemptionPolicy is the Policy for preempting pods with lower priority. One of Never, PreemptLowerPriority. Defaults to PreemptLowerPriority if unset. This field is beta-level, gated by the NonPreemptingPriority feature-gate. priority <integer> The priority value. Various system components use this field to find the priority of the pod. When Priority Admission Controller is enabled, it prevents users from setting this field. The admission controller populates this field from PriorityClassName. The higher the value, the higher the priority. priorityClassName <string> If specified, indicates the pod’s priority. “system-node-critical” and “system-cluster-critical” are two special keywords which indicate the highest priorities with the former being the highest priority. Any other name must be defined by creating a PriorityClass object with that name. If not specified, the pod priority will be default or zero if there is no default. readinessGates <[]Object> If specified, all readiness gates will be evaluated for pod readiness. A pod is ready when all its containers are ready AND all conditions specified in the readiness gates have status equal to “True” More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-network/0007-pod-ready%2B%2B.md restartPolicy <string> Restart policy for all containers within the pod. One of Always, OnFailure, Never. Default to Always. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle/#restart-policy runtimeClassName <string> RuntimeClassName refers to a RuntimeClass object in the node.k8s.io group, which should be used to run this pod. If no RuntimeClass resource matches the named class, the pod will not be run. If unset or empty, the “legacy” RuntimeClass will be used, which is an implicit class with an empty definition that uses the default runtime handler. More info: https://git.k8s.io/enhancements/keps/sig-node/runtime-class.md This is a beta feature as of Kubernetes v1.14. schedulerName <string> If specified, the pod will be dispatched by specified scheduler. If not specified, the pod will be dispatched by default scheduler. securityContext <Object> SecurityContext holds pod-level security attributes and common container settings. Optional: Defaults to empty. See type description for default values of each field. serviceAccount <string> DeprecatedServiceAccount is a depreciated alias for ServiceAccountName. Deprecated: Use serviceAccountName instead. serviceAccountName <string> ServiceAccountName is the name of the ServiceAccount to use to run this pod. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-service-account/ setHostnameAsFQDN <boolean> If true the pod’s hostname will be configured as the pod’s FQDN, rather than the leaf name (the default). In Linux containers, this means setting the FQDN in the hostname field of the kernel (the nodename field of struct utsname). In Windows containers, this means setting the registry value of hostname for the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\Tcpip\Parameters to FQDN. If a pod does not have FQDN, this has no effect. Default to false. shareProcessNamespace <boolean> Share a single process namespace between all of the containers in a pod. When this is set containers will be able to view and signal processes from other containers in the same pod, and the first process in each container will not be assigned PID 1. HostPID and ShareProcessNamespace cannot both be set. Optional: Default to false. subdomain <string> If specified, the fully qualified Pod hostname will be “<hostname>.<subdomain>.<pod namespace>.svc.<cluster domain>”. If not specified, the pod will not have a domainname at all. terminationGracePeriodSeconds <integer> Optional duration in seconds the pod needs to terminate gracefully. May be decreased in delete request. Value must be non-negative integer. The value zero indicates stop immediately via the kill signal (no opportunity to shut down). If this value is nil, the default grace period will be used instead. The grace period is the duration in seconds after the processes running in the pod are sent a termination signal and the time when the processes are forcibly halted with a kill signal. Set this value longer than the expected cleanup time for your process. Defaults to 30 seconds. tolerations <[]Object> If specified, the pod’s tolerations. topologySpreadConstraints <[]Object> TopologySpreadConstraints describes how a group of pods ought to spread across topology domains. Scheduler will schedule pods in a way which abides by the constraints. All topologySpreadConstraints are ANDed. volumes <[]Object> List of volumes that can be mounted by containers belonging to the pod. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/volumes |
上面给出了一个pod中spec所需字段
在更加深入的是
explain pod.spec.containers
| KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: containers <[]Object> DESCRIPTION: List of containers belonging to the pod. Containers cannot currently be added or removed. There must be at least one container in a Pod. Cannot be updated. A single application container that you want to run within a pod. FIELDS: args <[]string> Arguments to the entrypoint. The docker image’s CMD is used if this is not provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the container’s environment. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More info: command <[]string> Entrypoint array. Not executed within a shell. The docker image’s ENTRYPOINT is used if this is not provided. Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the container’s environment. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Cannot be updated. More info: env <[]Object> List of environment variables to set in the container. Cannot be updated. envFrom <[]Object> List of sources to populate environment variables in the container. The keys defined within a source must be a C_IDENTIFIER. All invalid keys will be reported as an event when the container is starting. When a key exists in multiple sources, the value associated with the last source will take precedence. Values defined by an Env with a duplicate key will take precedence. Cannot be updated. image <string> Docker image name. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images This field is optional to allow higher level config management to default or override container images in workload controllers like Deployments and StatefulSets. imagePullPolicy <string> Image pull policy. One of Always, Never, IfNotPresent. Defaults to Always if :latest tag is specified, or IfNotPresent otherwise. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#updating-images lifecycle <Object> Actions that the management system should take in response to container lifecycle events. Cannot be updated. livenessProbe <Object> Periodic probe of container liveness. Container will be restarted if the probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes name <string> -required- Name of the container specified as a DNS_LABEL. Each container in a pod must have a unique name (DNS_LABEL). Cannot be updated. ports <[]Object> List of ports to expose from the container. Exposing a port here gives the system additional information about the network connections a container uses, but is primarily informational. Not specifying a port here DOES NOT prevent that port from being exposed. Any port which is listening on the default “0.0.0.0” address inside a container will be accessible from the network. Cannot be updated. readinessProbe <Object> Periodic probe of container service readiness. Container will be removed from service endpoints if the probe fails. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes resources <Object> Compute Resources required by this container. Cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/configuration/manage-resources-containers/ securityContext <Object> Security options the pod should run with. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/policy/security-context/ More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/security-context/ startupProbe <Object> StartupProbe indicates that the Pod has successfully initialized. If specified, no other probes are executed until this completes successfully. If this probe fails, the Pod will be restarted, just as if the livenessProbe failed. This can be used to provide different probe parameters at the beginning of a Pod’s lifecycle, when it might take a long time to load data or warm a cache, than during steady-state operation. This cannot be updated. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/workloads/pods/pod-lifecycle#container-probes stdin <boolean> Whether this container should allocate a buffer for stdin in the container runtime. If this is not set, reads from stdin in the container will always result in EOF. Default is false. stdinOnce <boolean> Whether the container runtime should close the stdin channel after it has been opened by a single attach. When stdin is true the stdin stream will remain open across multiple attach sessions. If stdinOnce is set to true, stdin is opened on container start, is empty until the first client attaches to stdin, and then remains open and accepts data until the client disconnects, at which time stdin is closed and remains closed until the container is restarted. If this flag is false, a container processes that reads from stdin will never receive an EOF. Default is false terminationMessagePath <string> Optional: Path at which the file to which the container’s termination message will be written is mounted into the container’s filesystem. Message written is intended to be brief final status, such as an assertion failure message. Will be truncated by the node if greater than 4096 bytes. The total message length across all containers will be limited to 12kb. Defaults to /dev/termination-log. Cannot be updated. terminationMessagePolicy <string> Indicate how the termination message should be populated. File will use the contents of terminationMessagePath to populate the container status message on both success and failure. FallbackToLogsOnError will use the last chunk of container log output if the termination message file is empty and the container exited with an error. The log output is limited to 2048 bytes or 80 lines, whichever is smaller. Defaults to File. Cannot be updated. tty <boolean> Whether this container should allocate a TTY for itself, also requires ‘stdin’ to be true. Default is false. volumeDevices <[]Object> volumeDevices is the list of block devices to be used by the container. volumeMounts <[]Object> Pod volumes to mount into the container’s filesystem. Cannot be updated. workingDir <string> Container’s working directory. If not specified, the container runtime’s default will be used, which might be configured in the container image. Cannot be updated. |
container中需要的参数是我们生成一个Pod所需的必备字段
包含image和name是required
其中image是指定拉去的镜像的
我们可以如下的写
image:my-registry.example.com:5000/example/my-example:v1
image:my-registry.example.com registry 地址
5000 端口
example repostitory 名字
my-example:image名字
v1:image标签
基本上跟Docker的镜像书写一致
其次,在spec.containers中,有一个关键字段, imagePullPolicy
默认是IfNotPersent,除此外,还有Always和Never两个可选项
其分别代表着
IfNotPersent 如果本地仓库不存在则拉取
Always 总是尝试去拉取,如果拉取时发现本地存在了,则使用本地
Never,从不拉取,如果本地没有直接抛出Backoff的异常
而且,对于一些从私有镜像仓库拉取镜像的需求,我们可以考虑配置并使用对应的私钥
我们可以看对应的pord.secret中的imagePullSecrets的写法
| KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1 RESOURCE: imagePullSecrets <[]Object> DESCRIPTION: ImagePullSecrets is an optional list of references to secrets in the same namespace to use for pulling any of the images used by this PodSpec. If specified, these secrets will be passed to individual puller implementations for them to use. For example, in the case of docker, only DockerConfig type secrets are honored. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod LocalObjectReference contains enough information to let you locate the referenced object inside the same namespace. FIELDS: name <string> Name of the referent. More info: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/names/#names |
上面说了,如果需要查看对应的写法,可以看
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/containers/images#specifying-imagepullsecrets-on-a-pod
对应的文档中建议了写法,
| kubectl create secret -n hello docker-registry my-aliyun \
–docker-server=registry.cn.aliyuncs.com \ –docker-username=xxxxx\ –docker-password=xxxxx |
我们声明了一个secret,名字为 docker-registry
然后在Pod中声明
imagePullSecretes
-name: docker-registry
在官网上,也提供了最佳实践,基本如下
配置私有仓库有多种方案,以下是一些常用场景和建议的解决方案。
如果你需要访问多个仓库,可以为每个仓库创建一个 Secret。 kubelet 将所有 imagePullSecrets 合并为一个虚拟的 .docker/config.json 文件。 |
之后是关于容器的运行时相关命令
主要是容器中的ENV CMD EntryPoint如何在K8S中实现并使用
1. K8S中的ENV声明,我们仍然可以选择使用explain命令来进行查看
env <[]Object>
List of environment variables to set in the container. Cannot be updated.
很明显的可以看到,这是一个数组形式的env
更加明显的是
| FIELDS:
name <string> -required- Name of the environment variable. Must be a C_IDENTIFIER. value <string> Variable references $(VAR_NAME) are expanded using the previous defined environment variables in the container and any service environment variables. If a variable cannot be resolved, the reference in the input string will be unchanged. The $(VAR_NAME) syntax can be escaped with a double $$, ie: $$(VAR_NAME). Escaped references will never be expanded, regardless of whether the variable exists or not. Defaults to “”. valueFrom <Object> Source for the environment variable’s value. Cannot be used if value is not empty. |
很明显可以书写为如下格式
-name: hello
value: world
其次是对应的容器的启动命令
在containers中也可以进行声明,利用的是command和arg
对应的就是CMD和 EntryPoint
组合的方式基本如下
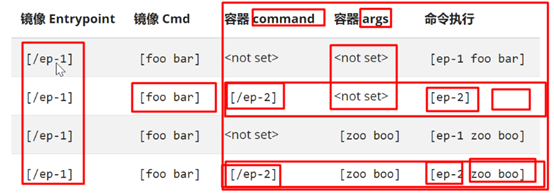
具体的格式可以参考如下链接
之后的相关的配置有
生命周期相关的钩子配置项,为容器的生命周期提供了两个相关配置项
1. PostStart:在容器创建后,执行,但并不保证执行时间段
2. PreStop:结束容器之前,负责执行相关指令
具体的书写,仍然采用explain进行查看
kubectl explain pod.spec.containers.lifecycle
其中很明确的给出了postStart和preStop两个生命线相关
其中每一个的书写格式基本一致
|
FIELDS: exec <Object> One and only one of the following should be specified. Exec specifies the action to take. httpGet <Object> HTTPGet specifies the http request to perform. tcpSocket <Object> TCPSocket specifies an action involving a TCP port. TCP hooks not yet |
支持exec执行shell
httpGet执行http请求
tcpSocket TCP请求
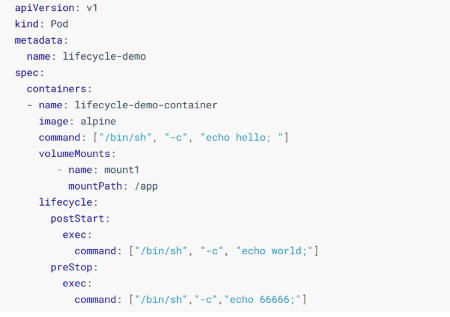
上面需要注意,postStart的启动时间不保证,而preStop则会在决定关闭的时候,立刻调用,一直等到preStop处理结束或者Pod的-grace-period超时,才删除容器
Pod中的资源限制则是直接在resources中声明
