本次,我们说下K8S中的对象
什么是K8S对象
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/concepts/overview/working-with-objects/kubernetes-objects/
K8S里面操作对象,就是K8S的对象,利用yamls声明,然后让k8s根据yaml声明创建出这
个对象
而之后,无论是什么对象,都会将应用程序中的数据存储在数据库中,也就是保存在etcd中,
我们可以利用kubectl describe 对象类型 对象名称,来K8S中的对象,因为所有资源实体,
都是对象,都会被保存在etcd中
其中包含了Controlled By 关键字,表示了被谁控制,下面就是被StatefulSet控制
除了元数据外就是Events表示,这个Pod经历的事件,Event的事例包括了Scheduler计算部署在哪个节点上
除此外,describe包含的信息有
集群中运行了哪些容器
集群中应用程序可用资源
集群中相关的策略,包括 重启策略 升级策略,容错策略
对于更加详细的信息,可以利用get pods 来将其输出为一个yaml文件格式,例如
kubectl get pod xxxx -o yaml -n dev
其中可以看到对象的spec和status,两个大类
spec 表示了对对象所期望的目标状态
status 表示了对象的实际状态
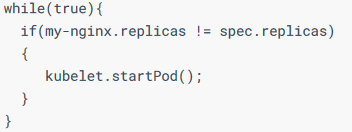
这里说下K8S的控制器如何保证目标状态和实际状态一致的方式,其实很简单,就是利用无限的for循环进行了监控,使得实际状态不断趋于目标状态
那么我们需要按照这个格式编写自己的yaml
对于yaml的编写,辅助手段包含如下
如果我们的集群中已经有了一个启动的pod,我们可以如下的获取yaml
kubectl get pod nginx-xx -o yaml
kubectl run tomcat-01 –image=tomcat –dry-run -o yaml #模拟运行
以及对于一个api-resource的探索可以使用 explain命令
这样我们基本能够得到一个基本的yaml文件
kind: Pod #资源类型 kubectl api-resources:可以获取到所有资源
apiVersion: v1 #同一个资源有可能有多个版本。看 kubectl api-resources提示的。
metadata: #每一个资源定义一些元数据信息
labels:
run: my-tomcat
name: my-tomcat
spec: #资源的规格(镜像名、镜像的环境变量信息等等)
containers:
– image: tomcat
name: my-tomcat
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
上面分为了typemeta,比如apiversion,kind ,关于这两个数据,可以利用kubect api-resource进行查看
其次是ObjectMeta,包含labels和name这样的数据
下面的spec是期望状态
对于这样的yaml文件,书写后进行部署的时候,推荐的方式是
kubectl apply -f ,而非 kubectl create -f
同样,删除推荐的操作为
kubectl delete -f
再次之后,我们说下K8S中的一个概念,也作为K8S的一个对象存在,就是其负责虚拟隔离的,namespace
在K8S中,存在3个默认命名空间
default kube-system kube-public
其作用为 方便不同的环境进行分别的部署测试,或者不同的产品进行空间隔离
虽然隔离了,但是只是虚拟的隔离,彼此之间网络可以通信
一个创建名称空间的yaml如下
| apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace metadata: name: <名称空间的名字> apiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: creationTimestamp: null name: k8s-03 spec: {} status: {} |
对于Kubernetes中的注解,我们略微的一说即可
在meta数据中声明即可
metadata:
annotations:
key1:value1
key2:value2
最后我们说下K8S一些相关的自动补完功能
可以首先在vscode中利用插件进行自动补完
vscode的plugin中搜索yaml和kubernetes template插件即可
idea也可以利用相关的插件
这样可以方便编写
其次是Linux 界面上的自动补完
官网有对应的介绍
https://kubernetes.io/zh/docs/tasks/tools/included/optional-kubectl-configs-bash-linux/
上面的介绍,我们简化为几个命令
yum install bash-completion
echo ‘source <(kubectl completion bash)’ >>~/.bashrc
kubectl completion bash >/etc/bash_completion.d/kubectl
source /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
所有的kubectl 命令参考
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubectl/kubectl-commands
| Basic Commands (Beginner): 初学者掌握的命令
create Create a resource from a file or from stdin. expose Take a replication controller, service, deployment or pod and expose it as a new Kubernetes Service run Run a particular image on the cluster set Set specific features on objects Basic Commands (Intermediate): 基础命令 explain Documentation of resources get Display one or many resources edit Edit a resource on the server delete Delete resources by filenames, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selector Deploy Commands: #部署用的命令 rollout Manage the rollout of a resource scale Set a new size for a Deployment, ReplicaSet or Replication Controller autoscale Auto-scale a Deployment, ReplicaSet, StatefulSet, or ReplicationController Cluster Management Commands: #集群管理的命令 certificate Modify certificate resources. cluster-info Display cluster info top Display Resource (CPU/Memory) usage. cordon Mark node as unschedulable uncordon Mark node as schedulable drain Drain node in preparation for maintenance taint Update the taints on one or more nodes Troubleshooting and Debugging Commands: # debug的命令 describe Show details of a specific resource or group of resources logs Print the logs for a container in a pod attach Attach to a running container |