测试代码性能的方法,查看那种解决方案的性能可能会更好的时候,基准测试会更有用,基准测试可以识别效率问题,测试不同的并发模式,工作池的大小和数量
我们看一组基准测试的函数,找出将整数值转为字符串的最快方法
在标准库中,有三种方法可以实现整数转为字符串
我们分别看一下,三种方式的测试
基准测试的文件名必须要以_test.go结尾,也必须要导入testing包
然后是一个基准测试函数
func BenchmarkSprintf(b *testing.B) {
number := 10
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
fmt.Sprintf(“%d”, number)
}
}
第一个基准测试函数,名为BenchmarkSprintf,基准测试函数以Benchmark开头,接受一个指向testing.B类型的指针作为唯一参数
然后测试的时候,利用for循环来将其转为字符串
fmt.Sprintf函数,将整数值转为字符串的函数
for循环调用要测试的函数,每次调用增加b.N的值,
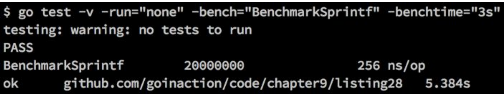
我们在运行的时候,加入-bench选项,代码基本如下
go test -v -run=”none” -bench=”BenchmarkSprintf”
go test中我们给run传递了none,none排除了所有的单元测试
运行得到如下的输出

上面说明了Sprintf运行的次数和性能
我们还能设置运行的时间,来进行测试,每次操作的时间
还有两个基准测试函数
// BenchmarkFormat provides performance numbers for the
// strconv.FormatInt function.
func BenchmarkFormat(b *testing.B) {
number := int64(10)
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
strconv.FormatInt(number, 10)
}
}
// BenchmarkItoa provides performance numbers for the
// strconv.Itoa function.
func BenchmarkItoa(b *testing.B) {
number := 10
b.ResetTimer()
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
strconv.Itoa(number)
}
}
都是基本使用b.N来控制每次调用时候迭代的次数
而且在其中,我们使用b.ResetTimer来重置计时器,然后我们尝试运行这串代码
goos: windows
goarch: amd64
BenchmarkSprintf
BenchmarkSprintf-8 19717318 59.3 ns/op
BenchmarkFormat
BenchmarkFormat-8 540629427 2.22 ns/op
BenchmarkItoa
BenchmarkItoa-8 537918792 2.20 ns/op
PASS
上面说明,我们使用三个函数,最慢的必然是Sprintf,然后就是Itoa和Format不相上下
我们还可以设置每次操作可以分配的内存次数
使用 -benchmem选项