对于一般的大集群来说,往往调度集群和文件集群是分开的,两者之间使用网络进行彼此的通信
那么我们需要进行搭建一个具有高可用的网络存储集群,这里首选的就是ceph
Ceph中存在对象存储,里面的存储方式键值对的存储方式,以及块设备,比如AWS的EBS/青云的云硬盘等
Ceph文件系统,比块存储有着更加丰富存储接口,需要考虑目录,文件属性等支持
我们来看下一个Ceph的存储集群中的构成

首先是Monitors,监控器,负责了管理之间的身份验证守护进程和客户端,通常需要三个监控器进行高可用配置
其次是Mangers,负责跟踪运行时指标和当前Cepth的集群状态,包括存储利用率等,一般需要两个进行高可用的配置
OSDS,负责进行实际的数据操作,需要三个进行高可用
MDS,负责存储元数据,也就是负责帮助系统找到对应的数据在哪个位置的组件
那么我们如何安装并使用这个存储集群呢?
其一为Cephadm,使用容器安装Ceph对应的管理组件
其二为Rook,部署在Kubernetes中,利用operator等对象集成Kubernetes的API
那么我们必然考虑使用Rook
对应的Rook的官方文档如下
https://rook.io/docs/rook/v1.8/quickstart.html
我们来看对应的安装指南
首先是一个必须的条件
需要一个干净的文件存储地址
– Raw devices (no partitions or formatted filesystems); 原始磁盘,无分区或者格式化
– Raw partitions (no formatted filesystem);原始分区,无格式化文件系统
这样就说明我们需要一个额外的挂载磁盘,供Ceph集群初始化
我们可以在云厂商中购买磁盘并挂载到对应的宿主机上
挂载完成云厂商会提示挂载的位置,我们也可以使用fdisk -l来看自己挂载的磁盘,比如/dev/vdc
然后进行相关的磁盘清理
dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/vdc bs=1M status=progress
然后就是Rook相关的部署及初始化了
首先需要done下来对应的yaml文件
$ git clone –single-branch –branch v1.8.6 https://github.com/rook/rook.git
cd rook/deploy/examples
下面分别有 crds.yaml,common.yaml,operator.yaml
然后修改operator.yaml
将镜像进行替换一下,修改yaml中的环境变量
# ROOK_CSI_CEPH_IMAGE: “quay.io/cephcsi/cephcsi:v3.5.1”
# ROOK_CSI_REGISTRAR_IMAGE: “k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-node-driver-registrar:v2.5.0”
# ROOK_CSI_RESIZER_IMAGE: “k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-resizer:v1.4.0”
# ROOK_CSI_PROVISIONER_IMAGE: “k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-provisioner:v3.1.0”
# ROOK_CSI_SNAPSHOTTER_IMAGE: “k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-snapshotter:v5.0.1”
# ROOK_CSI_ATTACHER_IMAGE: “k8s.gcr.io/sig-storage/csi-attacher:v3.4.0”
然后部署operator的yaml
kubectl create -f crds.yaml -f common.yaml -f operator.yaml
上面的operator其实是我们CRD自定义的处理器
CRD是K8S中的自定义资源类型,Rook就是自定义了些资源类型来进行使用的
利用这个operator,我们可以做到
Rook负责帮我们创建好StroageClass
然后我们创建PVC的时候,自定调用StorageClass中提供商,也就是Ceph集群操作
而Ceph中,根据PVC的定义,提供了Block Share FS等存储方式
比如Block,块存储,对应的就是我们之前NFS中的单一文件件,进行单节点的读写,适用于有状态的副本集
Share FS共享存储,对应的是ReadWriteMany 多节点读写,适用于无状态应用
这就是Rook和Ceph结合的能力
然后我们修改cluster.yaml,使用我们指定的磁盘当做存储节点
这是一个用于配置整个集群的yaml,我们的主要修改其中的组件配置,诸如
mon:
# Set the number of mons to be started. Generally recommended to be 3.
# For highest availability, an odd number of mons should be specified.
count: 3
# The mons should be on unique nodes. For production, at least 3 nodes are recommended for this reason.
# Mons should only be allowed on the same node for test environments where data loss is acceptable.
allowMultiplePerNode: false
上面就说了,我们配置monitor就需要三个进行高可用,我们就按照官方文档给予其三个monitor然后配置存储相关的关键性配置
| storage: # cluster level storage configuration and selection
useAllNodes: true useAllDevices: true #deviceFilter: config: # crushRoot: “custom-root” # specify a non-default root label for the CRUSH map # metadataDevice: “md0” # specify a non-rotational storage so ceph-volume will use it as block db device of bluestore. # databaseSizeMB: “1024” # uncomment if the disks are smaller than 100 GB # journalSizeMB: “1024” # uncomment if the disks are 20 GB or smaller # osdsPerDevice: “1” # this value can be overridden at the node or device level # encryptedDevice: “true” # the default value for this option is “false” # Individual nodes and their config can be specified as well, but ‘useAllNodes’ above must be set to false. Then, only the named # nodes below will be used as storage resources. Each node’s ‘name’ field should match their ‘kubernetes.io/hostname’ label. # nodes: # – name: “172.17.4.201” # devices: # specific devices to use for storage can be specified for each node # – name: “sdb” # – name: “nvme01” # multiple osds can be created on high performance devices # config: # osdsPerDevice: “5” # – name: “/dev/disk/by-id/ata-ST4000DM004-XXXX” # devices can be specified using full udev paths # config: # configuration can be specified at the node level which overrides the cluster level config # – name: “172.17.4.301” # deviceFilter: “^sd.” # when onlyApplyOSDPlacement is false, will merge both placement.All() and placement.osd onlyApplyOSDPlacement: false # The section for configuring management of daemon disruptions during upgrade or fencing. |
首先将odsPerDevice改为3个及以上个奇数
配置每个Node上的odsPerDevice的数量
然后是node配置信息
其中的name要和node上kubernetes.io/hostname标签上的一致
其次是devcie中的name,这个name要和挂载设备的路径一致
然后根据自我情况尝试替换镜像源
进行部署cluster.yaml即可
然后查看对应的组件,一定要包含如下的组件们
| #部署完成的最终结果一定要有这些组件
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE csi-cephfsplugin-provisioner-d77bb49c6-n5tgs 5/5 Running 0 140s csi-cephfsplugin-provisioner-d77bb49c6-v9rvn 5/5 Running 0 140s csi-cephfsplugin-rthrp 3/3 Running 0 140s csi-rbdplugin-hbsm7 3/3 Running 0 140s csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5b5cd64fd-nvk6c 6/6 Running 0 140s csi-rbdplugin-provisioner-5b5cd64fd-q7bxl 6/6 Running 0 140s rook-ceph-crashcollector-minikube-5b57b7c5d4-hfldl 1/1 Running 0 105s rook-ceph-mgr-a-64cd7cdf54-j8b5p 1/1 Running 0 77s rook-ceph-mon-a-694bb7987d-fp9w7 1/1 Running 0 105s rook-ceph-mon-b-856fdd5cb9-5h2qk 1/1 Running 0 94s rook-ceph-mon-c-57545897fc-j576h 1/1 Running 0 85s rook-ceph-operator-85f5b946bd-s8grz 1/1 Running 0 92m rook-ceph-osd-0-6bb747b6c5-lnvb6 1/1 Running 0 23s rook-ceph-osd-1-7f67f9646d-44p7v 1/1 Running 0 24s rook-ceph-osd-2-6cd4b776ff-v4d68 1/1 Running 0 25s rook-ceph-osd-prepare-node1-vx2rz 0/2 Completed 0 60s rook-ceph-osd-prepare-node2-ab3fd 0/2 Completed 0 60s rook-ceph-osd-prepare-node3-w4xyz 0/2 Completed 0 60s |
如果发现缺少对应的组件pod的时候,就可以删除部分的pod,来让其重新执行
然后我们需要访问dashboard,从而进行Rook集群的管理
不过需要注意,在Ceph的各个组件中
Osd是所有的都是进行工作的,Monitor也是同理
但是MGR是同一时间只有一个可以使用
所以如果有对应的Service直接进行LoadBalancer,那么会出现偶尔无法访问的情况
所以我们需要重新配置一个Ingress和Service进行访问
而整个的集群的Ingress 访问我们可以如下的配置
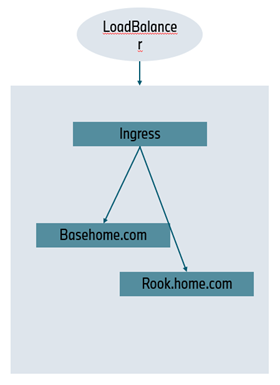
我们有一个IngressController,进行所有的Ingress配置的管理
然后是创建一个含有defaultBackend rule的Ingress,其来管理所有的TLS证书
诸如下面的操作,首先是创建一个secret
kubectl create secret tls itdachang.com –key tls.key –cert tls.crt
然后配置一个Ingress规则
| apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress metadata: name: itdachang-ingress namespace: default spec: tls: – hosts: – basehome.com – rook.hoem.com secretName: basehome.com defaultBackend: service: name: nginx-svc # ingress在这个名称空间,就找default名称空间的 port: number: 80 |
然后我们如果有了新的host需要进行TLS访问,这样既可
接下来是由于我们mgr组件的特殊性,我们需要按照如下的操作来配置一个新的Ingress
首先是部署一个nodeport来验证是否有不能访问的mgr
然后是创建一个自己的service,来管理自己需要管理的mgr
| apiVersion: v1
> kind: Service > metadata: > labels: > app: rook-ceph-mgr > ceph_daemon_id: a > rook_cluster: rook-ceph > name: rook-ceph-mgr-dashboard-active > namespace: rook-ceph > spec: > ports: > – name: dashboard > port: 8443 > protocol: TCP > targetPort: 8443 > selector: #service选择哪些Pod > app: rook-ceph-mgr > ceph_daemon_id: a > rook_cluster: rook-ceph > sessionAffinity: None > type: ClusterIP |
管理了对应的pod上标签
然后是创建了对应的Ingress
指向了对应的Servcie
| apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
> kind: Ingress > metadata: > name: ceph-rook-dash > namespace: rook-ceph > annotations: > nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: “HTTPS” > nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-snippet: | > proxy_ssl_verify off; > spec: > rules: > – host: rook.hoem.com > http: > paths: > – path: / > pathType: Prefix > backend: > service: > name: rook-ceph-mgr-dashboard-active > port: > number: 8443 |
到了Kubernetes中的实战环节
在rook上提供了多种模式的存储
比如Block块存储,还有Object,类似S3这类存储方式,还有Shared File System 创建一个文件系统供分享文件
我们首先看看对于块存储,是如何使用的
首先需要创建一个CRD,也就是Ceph中的自定义对象
| apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephBlockPool metadata: name: replicapool namespace: rook-ceph spec: failureDomain: host #容灾模式,host或者osd replicated: size: 2 #数据副本数量 |
然后是对应的storageClass,作为一个提供商进行存储绑定
| apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass #存储驱动 metadata: name: rook-ceph-block # Change “rook-ceph” provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if needed provisioner: rook-ceph.rbd.csi.ceph.com parameters: # clusterID is the namespace where the rook cluster is running clusterID: rook-ceph # Ceph pool into which the RBD image shall be created pool: replicapool # (optional) mapOptions is a comma-separated list of map options. # For krbd options refer # https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options # For nbd options refer # https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options # mapOptions: lock_on_read,queue_depth=1024 # (optional) unmapOptions is a comma-separated list of unmap options. # For krbd options refer # https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd/#kernel-rbd-krbd-options # For nbd options refer # https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/man/8/rbd-nbd/#options # unmapOptions: force # RBD image format. Defaults to “2”. imageFormat: “2” # RBD image features. Available for imageFormat: “2”. CSI RBD currently supports only `layering` feature. imageFeatures: layering # The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-rbd-node csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph # Specify the filesystem type of the volume. If not specified, csi-provisioner # will set default as `ext4`. Note that `xfs` is not recommended due to potential deadlock # in hyperconverged settings where the volume is mounted on the same node as the osds. csi.storage.k8s.io/fstype: ext4 # Delete the rbd volume when a PVC is deleted reclaimPolicy: Delete allowVolumeExpansion: true |
然后创建一个有状态应用,让其提一个PVC请求,来请求StorageClass来访问这个存储集群
| apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: StatefulSet metadata: name: sts-nginx namespace: default spec: selector: matchLabels: app: sts-nginx # has to match .spec.template.metadata.labels serviceName: “sts-nginx” replicas: 3 # by default is 1 template: metadata: labels: app: sts-nginx # has to match .spec.selector.matchLabels spec: terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 10 containers: – name: sts-nginx image: nginx ports: – containerPort: 80 name: web volumeMounts: – name: www mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html volumeClaimTemplates: – metadata: name: www spec: accessModes: [ “ReadWriteOnce” ] storageClassName: “rook-ceph-block” resources: requests: storage: 20Mi — apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: sts-nginx namespace: default spec: selector: app: sts-nginx type: ClusterIP ports: – name: sts-nginx port: 80 targetPort: 80 protocol: TCP |
这样就可以看到StorageClass中提供了对应的PV来供这些StatefulSet绑定
对应的Rook还提供了SharedFileSystem这样的能力,提供了RWX
| apiVersion: ceph.rook.io/v1
kind: CephFilesystem metadata: name: myfs namespace: rook-ceph # namespace:cluster spec: # The metadata pool spec. Must use replication. metadataPool: replicated: size: 3 requireSafeReplicaSize: true parameters: # Inline compression mode for the data pool # Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/nautilus/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compression compression_mode: none # gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool # for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size #target_size_ratio: “.5” # The list of data pool specs. Can use replication or erasure coding. dataPools: – failureDomain: host replicated: size: 3 # Disallow setting pool with replica 1, this could lead to data loss without recovery. # Make sure you’re *ABSOLUTELY CERTAIN* that is what you want requireSafeReplicaSize: true parameters: # Inline compression mode for the data pool # Further reference: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/nautilus/rados/configuration/bluestore-config-ref/#inline-compression compression_mode: none # gives a hint (%) to Ceph in terms of expected consumption of the total cluster capacity of a given pool # for more info: https://docs.ceph.com/docs/master/rados/operations/placement-groups/#specifying-expected-pool-size #target_size_ratio: “.5” # Whether to preserve filesystem after CephFilesystem CRD deletion preserveFilesystemOnDelete: true # The metadata service (mds) configuration metadataServer: # The number of active MDS instances activeCount: 1 # Whether each active MDS instance will have an active standby with a warm metadata cache for faster failover. # If false, standbys will be available, but will not have a warm cache. activeStandby: true # The affinity rules to apply to the mds deployment placement: # nodeAffinity: # requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: # nodeSelectorTerms: # – matchExpressions: # – key: role # operator: In # values: # – mds-node # topologySpreadConstraints: # tolerations: # – key: mds-node # operator: Exists # podAffinity: podAntiAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: – labelSelector: matchExpressions: – key: app operator: In values: – rook-ceph-mds # topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname will place MDS across different hosts topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname preferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: – weight: 100 podAffinityTerm: labelSelector: matchExpressions: – key: app operator: In values: – rook-ceph-mds # topologyKey: */zone can be used to spread MDS across different AZ # Use <topologyKey: failure-domain.beta.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster if your cluster is v1.16 or lower # Use <topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone> in k8s cluster is v1.17 or upper topologyKey: topology.kubernetes.io/zone # A key/value list of annotations annotations: # key: value # A key/value list of labels labels: # key: value resources: # The requests and limits set here, allow the filesystem MDS Pod(s) to use half of one CPU core and 1 gigabyte of memory # limits: # cpu: “500m” # memory: “1024Mi” # requests: # cpu: “500m” # memory: “1024Mi” # priorityClassName: my-priority-class mirroring: enabled: false |
以及一个StorageClass
| apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
kind: StorageClass metadata: name: rook-cephfs # Change “rook-ceph” provisioner prefix to match the operator namespace if needed provisioner: rook-ceph.cephfs.csi.ceph.com parameters: # clusterID is the namespace where operator is deployed. clusterID: rook-ceph # CephFS filesystem name into which the volume shall be created fsName: myfs # Ceph pool into which the volume shall be created # Required for provisionVolume: “true” pool: myfs-data0 # The secrets contain Ceph admin credentials. These are generated automatically by the operator # in the same namespace as the cluster. csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/provisioner-secret-namespace: rook-ceph csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-provisioner csi.storage.k8s.io/controller-expand-secret-namespace: rook-ceph csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-name: rook-csi-cephfs-node csi.storage.k8s.io/node-stage-secret-namespace: rook-ceph reclaimPolicy: Delete allowVolumeExpansion: true |
之后我们就可以创建多个无状态服务,来绑定这个StroageClass
| apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment metadata: name: nginx-deploy namespace: default labels: app: nginx-deploy spec: selector: matchLabels: app: nginx-deploy replicas: 3 strategy: rollingUpdate: maxSurge: 25% maxUnavailable: 25% type: RollingUpdate template: metadata: labels: app: nginx-deploy spec: containers: – name: nginx-deploy image: nginx volumeMounts: – name: localtime mountPath: /etc/localtime – name: nginx-html-storage mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html volumes: – name: localtime hostPath: path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai – name: nginx-html-storage persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nginx-pv-claim — apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: nginx-pv-claim labels: app: nginx-deploy spec: storageClassName: rook-cephfs accessModes: – ReadWriteMany ##如果是ReadWriteOnce将会是什么效果 resources: requests: storage: 10Mi |
这样就能做到了一个共享文件夹的分享使用
最后我们说下Rook的卸载
首先需要delete掉之前的yaml
Delete -f 之前的yaml
再执行如下命令
kubectl -n rook-ceph get cephcluster
kubectl -n rook-ceph patch cephclusters.ceph.rook.io rook-ceph -p ‘{“metadata”:{“finalizers”: []}}’ –type=merge
然后清除每个节点的
/var/lib/rook目录