初识Athena
在AWS的官网上,明确介绍了Athena的功能,其是一种交互式查询服务,让您能够轻松使用标准SQL。利用SQL来查询 Athena 指向 Amazon S3 中存储的数据,并开始使用标准 SQL 运行临时查询,然后在几秒钟内获得结果。
但是需要注意的是,Athena的查询需要花费金钱,且是按照查询数据集大小来量定花费,其本质是presto这样的一个大数据处理工具
对于Athena,支持使用
Amazon Web Services Management Console、JDBC 或 ODBC 连接、Athena API、Athena CLI、Amazon开发工具包,或者Amazon Tools for Windows PowerShell。
本次学习我们将聚焦于使用Amazon SDK for Java来进行使用Athena
不过在说明实际的代码之前,我们先说一下如何通过Web界面使用Athena
在进入AWS官方界面之后,首先确认开通了S3及Athena两个服务
我们先从S3创建一个桶,亦或者要求公司或者组织共享一个桶(关于共享就先不讲了,有缘介绍)
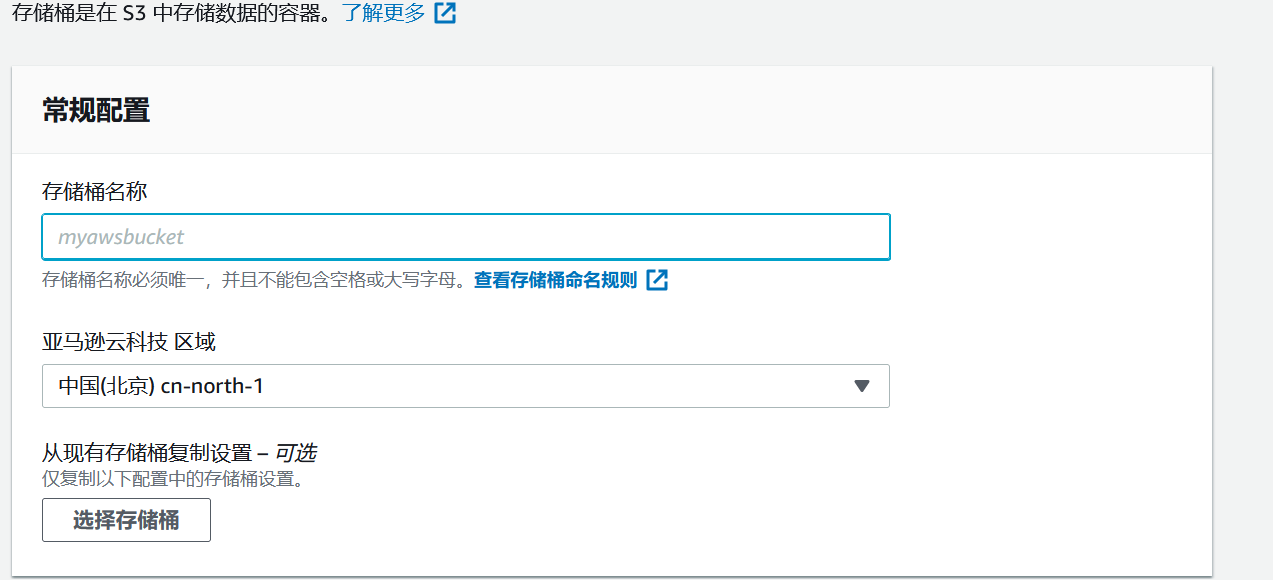
传入名字并且设置桶的访问策略之后就可以创建桶了(记住桶名称要求分区内唯一,类似阿里的OSS)
创建完成了,我们可以考虑在其中放入数据或者上传数据
Athena支持CSV、TSV、JSON 或文本文件等;此外,它还支持开源列式格式,如 Apache ORC 和 Apache Parquet。Athena 还支持 Snappy、Zlib、LZO 和 GZIP 格式的压缩数据。
比如我们上传一个CSV

内部数据为
aaa,22
张三,33
接下来就可以直接使用Athena去尝试读取了
首先在Athena中创建一个表,而这个DDL中,需要我们指定S3的存储位置
| CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE `test1`(
`name` string, `age` smallint) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ‘,’ STORED AS INPUTFORMAT ‘org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat’ OUTPUTFORMAT ‘org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveIgnoreKeyTextOutputFormat’ LOCATION ‘s3://test/data’ TBLPROPERTIES ( ‘has_encrypted_data’=’false’, ‘transient_lastDdlTime’=’1627033972’) |
像上面的数据,就指定了S3的位置为 test桶下的data文件夹内
然后就可以直接使用SQL来查询数据了
最基础的像
SELECT * FROM “test”.”test1″ limit 10;
返回结果为

如果知道文件名的话还可以执行如下的命令
SELECT * FROM “abeltest”.”test1″ where “$path” like ‘%111.csv’
获取到该文件下的结果
那么说完了基本的应用之后,说一下如何在Java中使用Athena进行查询
首先需要传入AWS提供的AccessKey和AccessId,然后创建AwsCredentialsProvider
| AwsCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider =
StaticCredentialsProvider.create(AwsBasicCredentials.create(“xxx”,”yyy”)); |
之后根据Athena的区域获取到对应的athenaClient
| AthenaClient athenaClient = AthenaClient.builder().region(Region.CN_NORTH_1)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider) .build(); |
在具体的执行过程中,需要传入的参数主要有sql,database,localResult
sql可以考虑使用StringBuilder亦或者format直接拼接,
database则是表所在的数据库
而localResult,则是将结果存放在的位置,在刚进入Athena网页的时候,会要求设置S3的结果存放位置,这个是类似的思路
具体获取结果,
则首先获取执行的executeId
| // The QueryExecutionContext allows us to set the Database.
QueryExecutionContext queryExecutionContext = QueryExecutionContext.builder() .database(database).build(); // The result configuration specifies where the results of the query should go in S3 and encryption options ResultConfiguration resultConfiguration = ResultConfiguration.builder() // You can provide encryption options for the output that is written. // .withEncryptionConfiguration(encryptionConfiguration) .outputLocation(athenaResult).build(); // Create the StartQueryExecutionRequest to send to Athena which will start the query. StartQueryExecutionRequest startQueryExecutionRequest = StartQueryExecutionRequest.builder() .queryString(sql) .queryExecutionContext(queryExecutionContext) .workGroup(workGroup) .resultConfiguration(resultConfiguration).build(); StartQueryExecutionResponse startQueryExecutionResponse = athenaClient.startQueryExecution(startQueryExecutionRequest); String executionId = startQueryExecutionResponse.queryExecutionId(); |
然后等待Athena执行完成,对于Athena的执行状态获取,可以执行如下的代码
| GetQueryExecutionRequest getQueryExecutionRequest = GetQueryExecutionRequest.builder()
.queryExecutionId(queryExecutionId).build(); GetQueryExecutionResponse executionResponse = athenaClient.getQueryExecution(getQueryExecutionRequest); return executionResponse.queryExecution().status().state().equals(QueryExecutionState.SUCCEEDED); |
之后根据executeId获取到最后的结果
| GetQueryResultsRequest getQueryResultsRequest = GetQueryResultsRequest.builder()
.queryExecutionId(queryExecutionId).build(); GetQueryResultsIterable getQueryResultsResults = athenaClient.getQueryResultsPaginator(getQueryResultsRequest); |
根据ExecuteId获取到了Results的迭代器,方便上层进行加工遍历
Athena的基本使用就说完了