桥接模式,也被叫做桥梁模式,是一种难以理解的模式了,而且有两种不同的理解方式,一种说明为将抽象和实现解耦,让其可以独立变化
除此外,还有一种解释方式,就是一个类拥有多种独立维度,通过组合的方式去代替继承关系,避免继承层面的指数级别爆炸
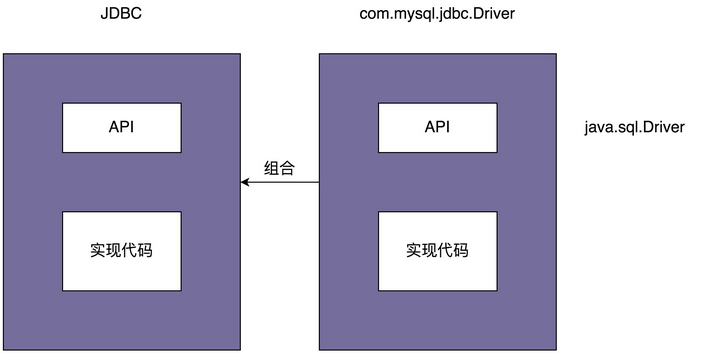
我们可以拿JDBC的驱动来举例说明,JDBC驱动是典型的桥接模式
|
Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”);//加载及注册JDBC驱动程序
String url = “jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/sample_db?user=root&password=your_password”; Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection(url); Statement stmt = con.createStatement(); String query = “select * from test”; ResultSet rs=stmt.executeQuery(query); while(rs.next()) { rs.getString(1); rs.getInt(2); } |
如果进行替换数据库,将MySQL数据库替换为Oracle数据库,只需要改Class.forName中的Driver类就可以了,甚至可以直接在配置文件中声明,在切换数据库的时候,都不用修改代码,修改配置文件就可以了
那么如何直接切换的数据库呢?
|
package com.mysql.jdbc;
import java.sql.SQLException; public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver { static { try { java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); } catch (SQLException E) { throw new RuntimeException(“Can’t register driver!”); } } /** * Construct a new driver and register it with DriverManager * @throws SQLException if a database error occurs. */ public Driver() throws SQLException { // Required for Class.forName().newInstance() } } |
在这个类的实际实现上,这个类执行Class.forName()的时候,实际上做了两件事,一是注册自己到DriverManager中,另一方面执行构造函数
那么DriverManager干了什么?
|
public class DriverManager {
private final static CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo> registeredDrivers = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<DriverInfo>(); //… static { loadInitialDrivers(); println(“JDBC DriverManager initialized”); } //… public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver) throws SQLException { if (driver != null) { registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver)); } else { throw new NullPointerException(); } } public static Connection getConnection(String url, String user, String password) throws SQLException { java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties(); if (user != null) { info.put(“user”, user); } if (password != null) { info.put(“password”, password); } return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass())); } //… } |
实际上,在这个类中,还是调用了Driver类去执行,只是负责了保存这个Driver类
那么,从上面的JDBC的实例来看,就可以发现JDBC本身就是抽象,具体的Driver就相当于是实现,两者独立开发,最后组合在一起,JDBC的所有操作,最后委托给了Driver执行
那么具体的应用也很简单了
我们之前写过了一个API接口监控告警的例子,根据不同的规则,触发不同的告警,支持邮件,短信,微信,语音电话,等通知
首先是最小最简模型
|
public enum NotificationEmergencyLevel {
SEVERE, URGENCY, NORMAL, TRIVIAL } public class Notification { private List<String> emailAddresses; private List<String> telephones; private List<String> wechatIds; public Notification() {} public void setEmailAddress(List<String> emailAddress) { this.emailAddresses = emailAddress; } public void setTelephones(List<String> telephones) { this.telephones = telephones; } public void setWechatIds(List<String> wechatIds) { this.wechatIds = wechatIds; } public void notify(NotificationEmergencyLevel level, String message) { if (level.equals(NotificationEmergencyLevel.SEVERE)) { //…自动语音电话 } else if (level.equals(NotificationEmergencyLevel.URGENCY)) { //…发微信 } else if (level.equals(NotificationEmergencyLevel.NORMAL)) { //…发邮件 } else if (level.equals(NotificationEmergencyLevel.TRIVIAL)) { //…发邮件 } } } //在API监控告警的例子中,我们如下方式来使用Notification类: public class ErrorAlertHandler extends AlertHandler { public ErrorAlertHandler(AlertRule rule, Notification notification){ super(rule, notification); } @Override public void check(ApiStatInfo apiStatInfo) { if (apiStatInfo.getErrorCount() > rule.getMatchedRule(apiStatInfo.getApi()).getMaxErrorCount()) { notification.notify(NotificationEmergencyLevel.SEVERE, “…”); } } } |
上面可以看出,我们具有多种告警级别,以及多种告警手段,这样我们if-else判断的时候,逻辑很复杂,我们可以发送的渠道抽离出来,形成一个信息发送接口
这个信息发送接口,而且可以实现多个信息发送类,对于实际的组合,可以随意拼接,这种拼接方式,就是一种桥梁的组合方式,
而且指定如何拼接,可以动态的去指定,那么代码可以改为如下
|
public interface MsgSender {
void send(String message); } public class TelephoneMsgSender implements MsgSender { private List<String> telephones; public TelephoneMsgSender(List<String> telephones) { this.telephones = telephones; } @Override public void send(String message) { //… } } public class EmailMsgSender implements MsgSender { // 与TelephoneMsgSender代码结构类似,所以省略… } public class WechatMsgSender implements MsgSender { // 与TelephoneMsgSender代码结构类似,所以省略… } public abstract class Notification { protected MsgSender msgSender; public Notification(MsgSender msgSender) { this.msgSender = msgSender; } public abstract void notify(String message); } public class SevereNotification extends Notification { public SevereNotification(MsgSender msgSender) { super(msgSender); } @Override public void notify(String message) { msgSender.send(message); } } public class UrgencyNotification extends Notification { // 与SevereNotification代码结构类似,所以省略… } public class NormalNotification extends Notification { // 与SevereNotification代码结构类似,所以省略… } public class TrivialNotification extends Notification { // 与SevereNotification代码结构类似,所以省略… } |
对于桥接来说,我个人认为,就是一个类中有多个属性,我们可以将这些属性分开来设计,彼此之间不具有关联,这些个属性就可以认为是多个维度,可以说,就是所谓的抽象,而这个类,就是讲这些属性连接起来的桥,这就是桥接模式,也就是真正实现这个类时候,属性需要注入真正的实现类.例如:一个商品可以对应的多种属性,不同属性就是多个维度,这些属性在这个商品中可以是个抽象的概念,但是在扩展的时候,扩展出了实现类,而这个商品负责连接他们,做到了真正意义上的解耦.突然想到了小岛秀夫的死亡搁浅,所谓的桥接型游戏