我们说了一些经典的设计模式,我们来说一下MyBatis中涉及的职责链模式和代理模式,其和Servlet Filter,Spring Interceptor拦截器类似,都是为了框架的扩展性,都可以归纳于职责链模式
不过,相比较于Servlet Filter和Spring Interceptor,MyBatis Plugin的实现借助于了代理模式的职责链
MyBatis Plugin和Servlet Filter及Spring Interceptor的功能类似,都是不修改原有流程代码的情况下,执行一些额外的代码逻辑,唯一区别在于拦截的位置不一样的,Servlet Filter是对于Servlet的请求,Spring Interceptor主要拦截Spring的Bean方法,比如Controller类的方法等,而MyBatis Plugin是对SQL执行过程的拦截
假如,我们需要统计应用中每个SQL的执行耗时,如果使用MyBatis Plugin来实现的话,需要定义一个SqlCostTimeInterceptor类,实现MyBaits的Interceptor接口,并且,在MyBaits的全局配置文件中,声明这个拦截器
| @Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = “query”, args = {Statement.class, ResultHandler.class}), @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = “update”, args = {Statement.class}), @Signature(type = StatementHandler.class, method = “batch”, args = {Statement.class})}) public class SqlCostTimeInterceptor implements Interceptor { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SqlCostTimeInterceptor.class); @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { Object target = invocation.getTarget(); long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); StatementHandler statementHandler = (StatementHandler) target; try { return invocation.proceed(); } finally { long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() – startTime; BoundSql boundSql = statementHandler.getBoundSql(); String sql = boundSql.getSql(); logger.info(“执行 SQL:[ {} ]执行耗时[ {} ms]”, sql, costTime); } } @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { System.out.println(“插件配置的信息:”+properties); } } <!– MyBatis全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml –> <plugins> <plugin interceptor=”com.xzg.cd.a88.SqlCostTimeInterceptor”> <property name=”someProperty” value=”100″/> </plugin> </plugins> |
我们首先从@Intercepts这一部分看起,不管是拦截器,过滤器还是插件,都需要明确的标明拦截的方法,@Intercepts注解就是这个作用,其中@Intercepts注解可以嵌套多个@Signature,一个@Signature注解标明一个要拦截的目标方法,如果要拦截多个,可以编写多个@Signature注解
@Signature注解包含三个元素,type,method,args,type指明要拦截的类,method指明方法名字,args指明方法的参数列表,通过这三个元素,标明一个要拦截的方法
但是具有被拦截的方法,只有如下的几个
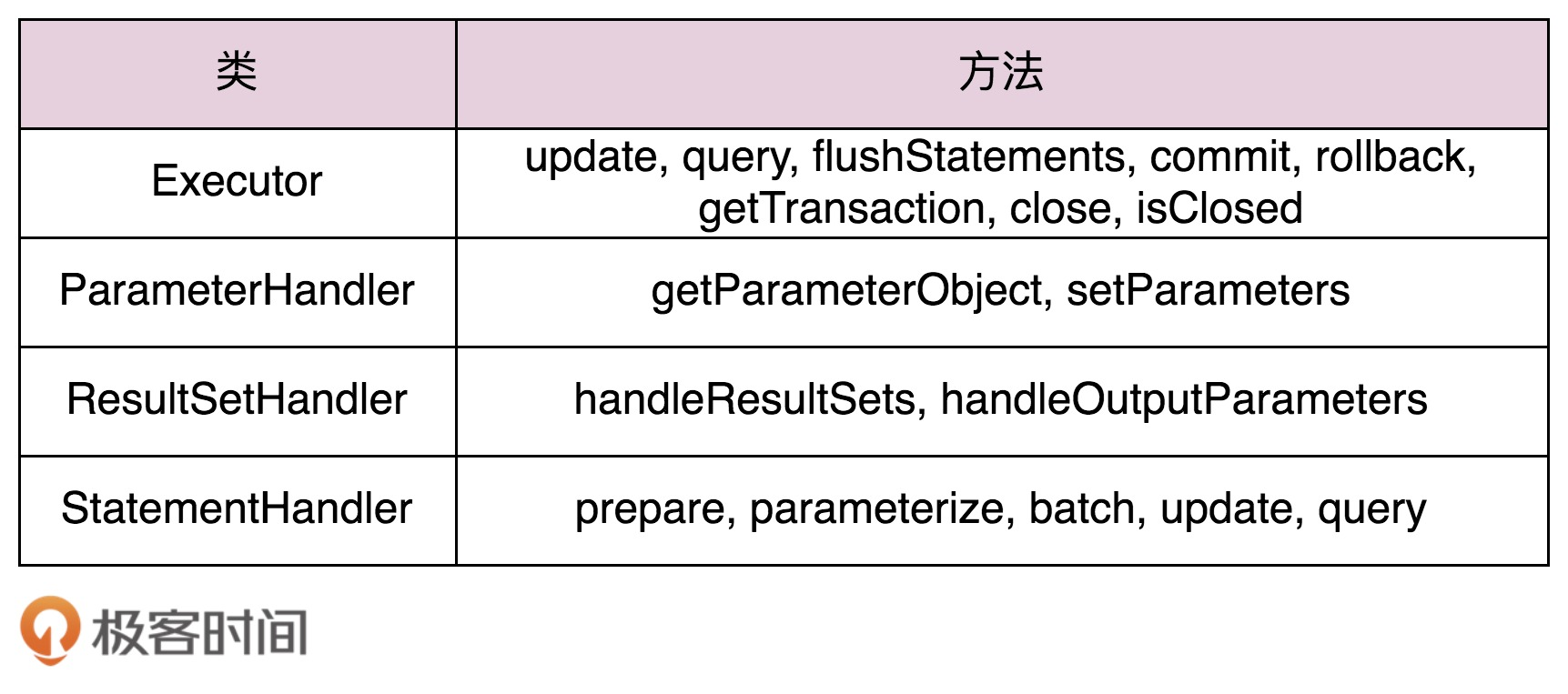
这几个方法就是MyBatis中的执行流程涉及的方法,Mybatis通过Executor来执行SQL的,Executor会创建StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,,ResultSetHandler三个对象,并且,首先使用ParameterHandler设置了SQL中占位符参数,然后使用StatementHandler来执行SQL语句,最后使用ResultHandler来封装结果,所以,我们只需拦截这几个类的方法,就可以控制SQL执行流程了
利用了MyBatis Plugin,我们还能做很多事情,比如分库分表,自动分页,数据加密解密等
MyBatis Plugin的设计和实现中,设计了动态代理模式实现了职责链的,一般来说,职责链汇总都会存在两个部分,处理器Handler,处理器链HandlerChain两个部分,Servlet Filter中就是Filter和Filter Chain两个部分,对应到MyBaits中就是Interceptor和InterceptorChain,当然,在因为涉及了动态代理,所以还包含了一个非常重要的类,Plugin,用于动态生成被拦截的类的动态代理
集成了MyBaits的应用启动的时候,会读取全局配置文件,mybatis-config.xml,解析出Interceptor,并且注入到Configuration类的InterceptorChain对象中
对应的源码如下
| public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
//解析配置 private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //省略部分代码… pluginElement(root.evalNode(“plugins”)); //解析插件 } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException(“Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: ” + e, e); } } //解析插件 private void pluginElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { String interceptor = child.getStringAttribute(“interceptor”); Properties properties = child.getChildrenAsProperties(); //创建Interceptor类对象 Interceptor interceptorInstance = (Interceptor) resolveClass(interceptor).newInstance(); //调用Interceptor上的setProperties()方法设置properties interceptorInstance.setProperties(properties); //下面这行代码会调用InterceptorChain.addInterceptor()方法 configuration.addInterceptor(interceptorInstance); } } } } // Configuration类的addInterceptor()方法的代码如下所示 public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptorChain.addInterceptor(interceptor); } |
我们来看看Interceptor和InterceptorChain两个类的代码,Interceptor的setProperties的方法是个单纯的Setter方法,为了方便配置去配置一些属性值,在Interceptor中,有着intercept()和plugin()函数,在InterceptorChain类中的pluginAll()函数,是最核心的三个函数,我们过会解释
| public class Invocation {
private final Object target; private final Method method; private final Object[] args; // 省略构造函数和getter方法… public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException { return method.invoke(target, args); } } public interface Interceptor { Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable; Object plugin(Object target); void setProperties(Properties properties); } public class InterceptorChain { private final List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<Interceptor>(); public Object pluginAll(Object target) { for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); } return target; } public void addInterceptor(Interceptor interceptor) { interceptors.add(interceptor); } public List<Interceptor> getInterceptors() { return Collections.unmodifiableList(interceptors); } } |
这样,解析完成配置文件后,所有的Interceptor都加载到了InterceptorChain之中,这些拦截器如何被触发的呢?
这个可以借鉴到我们执行SQL过程中,MyBatis会创建Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler这几个类的对象
创建的过程在Configuration类中
| public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; } public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) { ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql); parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler); return parameterHandler; } public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds); resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler); return resultSetHandler; } public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; } |
从上面的代码中,可以发现,在类的创建过程中调用了InterceptorChain的pluginAll()方法,这个方法中,会嵌套调用InterceptorChain上每个Interceptor的plugin()方法,plugin()是一个接口方法,TImeCost拦截器的具体实现是去调用了Plugin的wrap()方法实现的,wrap方法代码如下
| // 借助Java InvocationHandler实现的动态代理模式
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler { private final Object target; private final Interceptor interceptor; private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap; private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { this.target = target; this.interceptor = interceptor; this.signatureMap = signatureMap; } // wrap()静态方法,用来生成target的动态代理, // 动态代理对象=target对象+interceptor对象。 public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) { Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor); Class<?> type = target.getClass(); Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap); if (interfaces.length > 0) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance( type.getClassLoader(), interfaces, new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)); } return target; } // 调用target上的f()方法,会触发执行下面这个方法。 // 这个方法包含:执行interceptor的intecept()方法 + 执行target上f()方法。 @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass()); if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) { return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args)); } return method.invoke(target, args); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e); } } private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) { Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class); // issue #251 if (interceptsAnnotation == null) { throw new PluginException(“No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor ” + interceptor.getClass().getName()); } Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value(); for (Signature sig : sigs) { Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(sig.type()); if (methods == null) { methods = new HashSet<Method>(); signatureMap.put(sig.type(), methods); } try { Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args()); methods.add(method); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new PluginException(“Could not find method on ” + sig.type() + ” named ” + sig.method() + “. Cause: ” + e, e); } } return signatureMap; } private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) { Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<Class<?>>(); while (type != null) { for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) { if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) { interfaces.add(c); } } type = type.getSuperclass(); } return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]); } } |
plugin是借助了Java InvocationHandler实现的动态代理类,代理给target对象添加上Interceptor功能,要代理的target对象就是Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler这四个类的对象,wrap()这个静态方法就是生成target对象的动态代理对象的
当然,并不是无脑的生成target对象,而是只有@Signature注解要连接的类包含target对象的时候,才能生成.这个在wrap()函数的开头就会检验是否有对应的interface
Mybatis的职责链模式的实现方式比较特殊,会对同一个目标对象嵌套多次代理,从而做到职责链的拦截功能
| public Object pluginAll(Object target) {
// 嵌套代理 for (Interceptor interceptor : interceptors) { target = interceptor.plugin(target); // 上面这行代码等于下面这行代码,target(代理对象)=target(目标对象)+interceptor(拦截器功能) // target = Plugin.wrap(target, interceptor); } return target; } // MyBatis像下面这样创建target(Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler),相当于多次嵌套代理 Object target = interceptorChain.pluginAll(target); |
当执行Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler四个类上面的某个方法的时候,mybatis都会嵌套执行每层代理对象Plugin对象上的invoke()方法,然后invoke()方法会先执行代理对象的interceptor的intercept()函数,最后一步步走到原始的4个类的对象上
本章重点:
我们看了利用了职责链模式和动态代理模式实现的MyBatis Plugin,至此,职责链模式可以适用的三种场景,过滤器,拦截器,插件
职责链模式的实现一般包含处理器和处理器链两部分,对应出来的就是Servlet Filter和FilterChain,除此外,在mybatis中,还有重要的实现类,Plugin类,用于生成被拦截的对象的动态代理
课后思考
Servlet Filter,Spring Interceptor都可以用来拦截用户自定义的类的方法,但是Mybatis Plugin可以拦截的只有Executor,StatementHandler,ParameterHandler,ResultSetHandler这四个类的方法,为什么Mybatis不拦截用户自定义的类的方法呢?